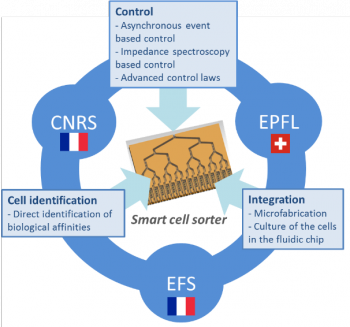
CNRS involves its two main institutes in the field of Microrobotics: FEMTO-ST in Besancon and ISIR in Paris. FEMTO-ST Institute is a joint research unit involving 700 persons which is affiliated with the CNRS, UFC, ENSMM and UTBM. ISIR Institute is hosted by the Université Pierre et Marie Curie (UPMC) and associated with the CNRS. CNRS is one of the biggest team in the world focusing on microrobotics. It has a strong experience on closed loop control of dielectrophoresis and on advanced vision tools.
CNRS involves its two main institutes in the field of Microrobotics: FEMTO-ST in Besancon and ISIR in Paris. FEMTO-ST Institute is a joint research unit involving 700 persons which is affiliated with the CNRS, UFC, ENSMM and UTBM. ISIR Institute is hosted by the Université Pierre et Marie Curie (UPMC) and associated with the CNRS. CNRS is one of the biggest team in the world focusing on microrobotics. It has a strong experience on closed loop control of dielectrophoresis and on advanced vision tools.
![]() EPFL (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne) emphasizes both fundamental research and engineering applications and offers real development opportunities to the economy. It features one of the largest state of the art academic clean room facilities in the world. The Laboratory for Microsystems 4 (LMIS4) is a multidisciplinary research unit that focuses on the development of technologies and systems for miniaturized biomedical applications. LMIS4 has experience with dielectrophoretic actuation for cell sorting and analysis, as well as with impedance spectroscopy measurements for cell analysis.
EPFL (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne) emphasizes both fundamental research and engineering applications and offers real development opportunities to the economy. It features one of the largest state of the art academic clean room facilities in the world. The Laboratory for Microsystems 4 (LMIS4) is a multidisciplinary research unit that focuses on the development of technologies and systems for miniaturized biomedical applications. LMIS4 has experience with dielectrophoretic actuation for cell sorting and analysis, as well as with impedance spectroscopy measurements for cell analysis.
![]() The Etablissement Français du Sang (EFS) [French National Blood Service] is the only civilian blood transfusion organization in France. Research at the EFS is contributing to the development of new cell-therapy products to regenerate damaged tissues or provide immunity against a tumor or pathogen. The research activities in the laboratory UMR1098 INSERM are dedicated to the development of innovative cell therapy protocols to improve outcomes in transplantation and oncology. EFS Bourgogne Franche Comté and UMR 1098 has promoted several clinical trials such as (i) gene therapy (suicide gene transfer) to optimize hematopoietic cell transplantation, (ii) natural killer cell adoptive transfer in colon cancers. Within this context, the potential of lymphocyte cell-therapy engineering and the improvement of anti-tumor lymphocyte amplification and differentiation methods are areas that are being actively explored.
The Etablissement Français du Sang (EFS) [French National Blood Service] is the only civilian blood transfusion organization in France. Research at the EFS is contributing to the development of new cell-therapy products to regenerate damaged tissues or provide immunity against a tumor or pathogen. The research activities in the laboratory UMR1098 INSERM are dedicated to the development of innovative cell therapy protocols to improve outcomes in transplantation and oncology. EFS Bourgogne Franche Comté and UMR 1098 has promoted several clinical trials such as (i) gene therapy (suicide gene transfer) to optimize hematopoietic cell transplantation, (ii) natural killer cell adoptive transfer in colon cancers. Within this context, the potential of lymphocyte cell-therapy engineering and the improvement of anti-tumor lymphocyte amplification and differentiation methods are areas that are being actively explored.